| CAS
NO. |
527-07-1 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
208-407-7 |
| FORMULA |
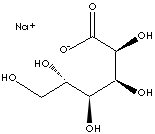
HOCH2[CH(OH)]4COONa |
| MOL
WT. |
218.14 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2918.16.2000 |
|
TOXICITY
|
Rabbit LDLo (intravenous):
7630mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
D-Gluconic acid, sodium salt; |
| D-Gluconic acid monosodium salt; Glonsen; Gluconato di sodio; Monosodium D-gluconate; Sodium (2R,3S,4R,5R')-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate; 2,3,4,5,6-Pentahydroxycaproic acid sodium salt; Sodium Gluconate; Other RN: 15537-84-5, 22808-65-7, 24551-74-4, 252255-37-1, 526-95-4 (Parent) |
| SMILES |
O[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](CO)O)O)[C@@H](C(=O)[O-])O.[Na+] |
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
Gluconate, Replenisher, UNII-R6Q3791S76. Carbohydrate, Monosaccharide, Sequestering agent |
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to slightly yellow crystalline powder |
| MELTING POINT |
170 - 175 (Decomposes) |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Soluble (5.90E+05 mg/l at 25 C) |
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
Insoluble in alcohol, benzene |
| pH |
6.5 - 8.0 (10% Sol.) |
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
| log Pow |
-5.99 (Octanol-water) |
| OH RATE |
3.81E-11 (cm3/molecule-sec
at 25 C Atmospheric) |
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
| NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1; Flammability: 0; Instability: 0 |
| REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
|
|
Gluconic acid is a polyhydroxycarboxylic acid
with six carbon length. It is derived from glucose by
oxidation of the aldehyde group on the C-1 to a carboxyl group. It is abundant
in plants, fruits and other foodstuffs. Commercially the physiological d-form
gluconic acid is prepared by fermentation process. It has a carboxylic group and
five hydroxy groups, and thus is a good chelator particularly in alkaline
conditions. Chelation is a chemical combination with a metal in complexes in
which the metal is part of a ring. Organic ligand is called chelator or
chelating agent, the chelate is a metal complex. The larger number of ring
closures to a metal atom is the more stable the compound. Chelation is applied
in metal complex chemistry, organic and inorganic chemistry, biochemistry, and
environment protection. It is used in chemotherapeutic treatments for metal
poisoning. Chelating agents offers a wide range of sequestrants to control metal
ions in aqueous systems. By forming stable water soluble complexes with
multivalent metal ions, chelating agents prevent undesired interaction by
blocking normal reactivity of metal ions. Heavy metals are chelated in alkaline
solution and their interferences are eliminated gluconic acid. Concentrated
gluconic acid solution contains certain lactone structure, a neutral cyclic
ester, showing antiseptic property. Gluconic acid and its derivatives (salts or
esters) are used in the formulation of pharmaceuticals, foods, and cosmetics as
mineral supplements to prevent the deficiency and as buffer salts. They are used
as ingredients in various hygienic products. In industrial applications, they
are used for scale removal in metal cleanings, industrial and household cleaning
compounds including mouth washer, metal finishing, water treatments, and as
paper and textile auxiliaries. Wikipedia
Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sequestrant
http://www.food.gov.uk/multimedia/pdfs/elist_numbers.pdf
LIST
OF ADDITIVES CURRENTLY PERMITTED IN FOOD IN THE EUROPEAN
UNION AND THEIR E NUMBERS.
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
USP/FCC/EP
|
|
APPEARANCE
|
white to off-white powder |
|
IDENTIFICATION |
pass
(Test A, Test B)
|
|
ASSAY
|
98.0
- 102.0%
|
|
SPECIFIC
ROTATION
|
11.5
- 12.5° |
|
ARSENIC
|
3ppm
max
|
|
LEAD
|
10ppm
max
|
|
WATER
|
11.6%
max
|
|
REDUCING
MATTERS
|
0.5%
max
|
|
LOSS
ON DRYING
|
3.0%
max
|
|
OVI
|
pass
test (Organic Volatile Impurities)
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
Not
regulated |
| UN
NO. |
|
|
OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard
Symbols: n/a, Risk Phrases: n/a, Safety Phrases: 24/25-26-36/37/39 |
